In this dynamic era of AI and digital technology, Human-Centric UX Design transcends being a mere trend to become a fundamental necessity. It’s not only about refining interfaces but pioneering a transformative wave in AI development, aligning technology with human intuitiveness and needs. Additionally, embracing a Human-Centric Design philosophy is vital for elevating company projects and products. Our blogpost today will dive further into the crucial role this approach plays in IT product success, discussing how integrating a human-focused perspective in technology is essential for advancement.
Understand Human-Centric UI/UX Design


Definition


Human-Centric UI/UX Design is a design philosophy that places the user at the forefront of the design process. This approach seeks to deeply understand and cater to the users’ needs, emotions, and behaviors. It emphasizes creating interfaces and experiences that are not only functional and efficient but also genuinely resonate with the users, enhancing their interaction with technology in a meaningful way. Human-centric UX design transcends a mere process; it embodies a mindset that prioritizes the end-user’s experience in every interaction with digital interfaces. Recognizing each click, swipe, or tap as a meaningful interaction, this approach aims to create experiences that deeply resonate with the human element, acknowledging that the true measure of success lies in the satisfaction and engagement of the user.
Traditional UX Design versus Human-Centric UX Design


Traditional UX Design primarily focuses on the usability and functionality of a product, emphasizing technical aspects and aesthetics. It typically revolves around creating efficient and intuitive user interfaces, ensuring that the product is easy to use and navigate, focuses on what features to include and how users should interact with the interface. Human-Centric UX Design, in contrast, goes beyond these technicalities, delving into the why features – emotional and psychological aspects of the user experience. This approach involves a deep understanding of the users’ needs, behaviors, motivations, and overall context. It aims to create products that not only function well but also resonate emotionally with users, making their experience more meaningful and engaging. This method often involves extensive user research, empathy, and designing for inclusivity and accessibility. While traditional UX design is often more feature and solution-oriented, human-centric design is more user and experience-oriented. It seeks not just to solve a problem but to enhance the overall user experience in a way that is deeply connected to the users’ personal and emotional needs.
The Roles of Human-Centric UX Design


Inclusivity in Design: Addressing Diverse User Needs
Human-Centric Design stands as a pivotal approach in fostering inclusivity within digital experiences. By prioritizing early user involvement, designers gain invaluable insights into the diverse needs and preferences of their audience. This methodology acknowledges that users span a wide spectrum in terms of age, expertise, and preferences. The emphasis on inclusivity ensures that design decisions resonate with a broad range of users, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
Integrating Feedback: Continuous Improvement Through Human-Centric Design
The iterative nature of Human-Centric UX Design aligns seamlessly with contemporary industry practices. By integrating continuous feedback loops, designers create a dynamic design process that evolves in response to user insights. This approach not only enhances the overall quality of products but also ensures their relevance over time. User feedback becomes a catalyst for innovation, driving improvements and refinements that are directly informed by the experiences and preferences of the end-users.
Educational Perspectives and Ethics in Human-Centric Design
Beyond its practical applications, Human-Centric Design necessitates a thoughtful and ethical approach. Designers are tasked with considering the broader societal implications of their work. Recent discussions within the field highlight the increasing concern among users about data privacy and ethical technology use. This underlines the ethical imperative for designers to balance the pace of design with a deeper introspection, ensuring that the solutions they create align with ethical principles and contribute positively to the user’s environment.
The Human-Centered Design Process
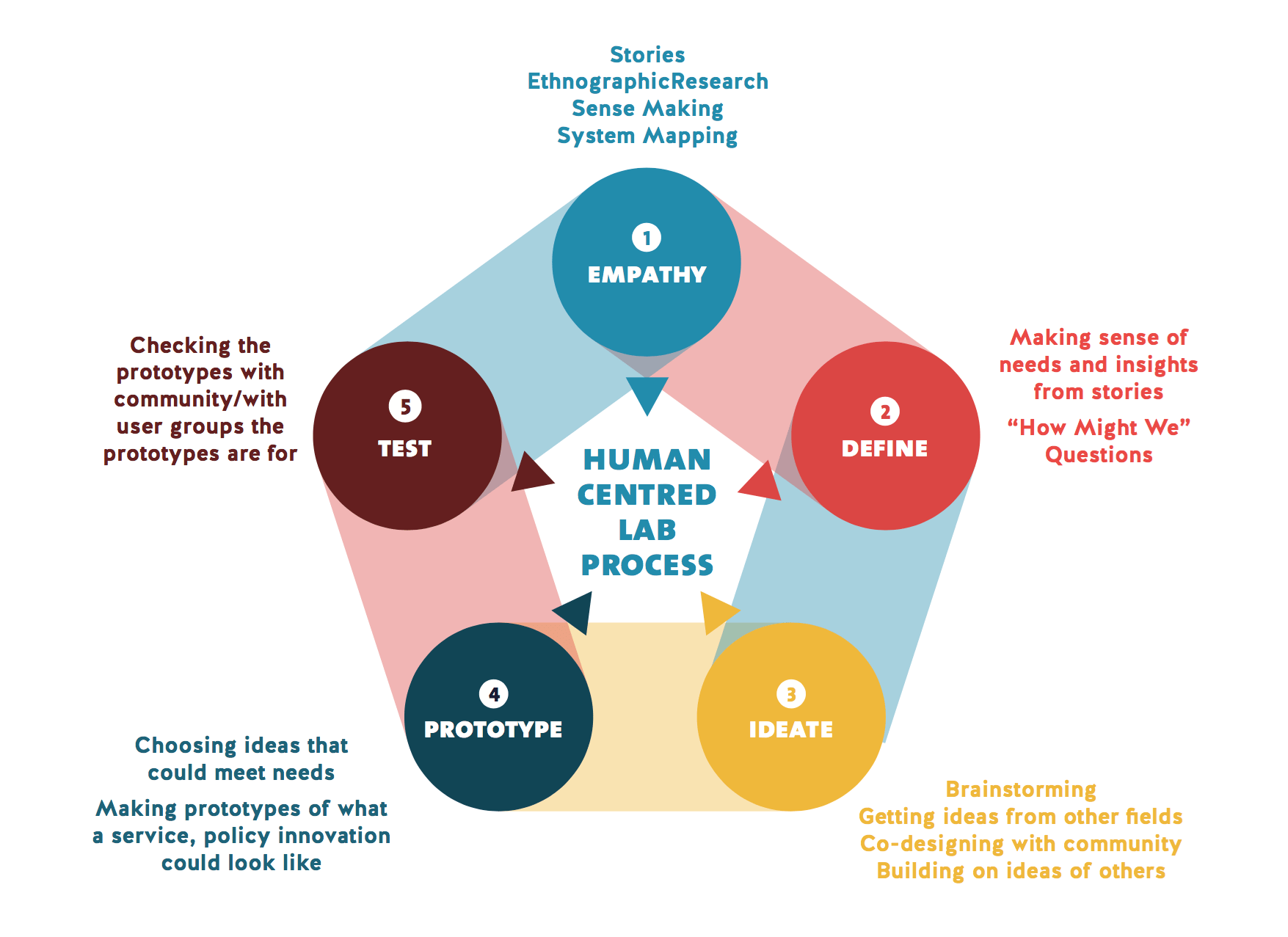

Stage 1 – Empathy: Understanding User Perspectives
The foundation of Human-Centered Design lies in empathizing with the users. This involves immersing oneself in the user’s environment, observing their behaviors, and actively listening to their needs and challenges. Empathy enables designers to gain a deep understanding of the user’s motivations and frustrations, forming the basis for informed decision-making throughout the design process.
Stage 2 – Define: Framing the Problem
Once a thorough understanding of the user’s experience is established, the next step is to define the problem. This involves distilling the insights gathered during the empathy stage into a clear and concise problem statement. By precisely defining the problem, designers set the stage for focused ideation and solution development. This step ensures that the design process remains targeted and aligned with the user’s actual needs.
Stage 3 – Ideate: Generating Creative Solutions
Ideation is the phase where creativity takes center stage. Designers, armed with a well-defined problem statement, engage in brainstorming sessions to generate a multitude of ideas. The emphasis is on quantity, encouraging a diverse range of solutions. This stage encourages thinking beyond conventional boundaries, fostering innovation and pushing designers to explore novel concepts that might otherwise be overlooked.
Stage 4 – Prototype: Bringing Ideas to Life
Prototyping involves transforming selected ideas from the ideation stage into tangible, visual representations. These representations can range from low-fidelity sketches to high-fidelity interactive models. Prototypes serve as a means to test and validate design concepts quickly and iteratively. This stage allows designers to receive early feedback, identify potential challenges, and refine their solutions before investing extensive resources in development.
Stage 5 – Test: Iterative Validation with Users
The testing stage involves putting prototypes in front of actual users and collecting feedback. This iterative process allows designers to gauge how well their solutions align with user expectations and needs. Testing is not a one-time event; rather, it is a continuous loop that informs further refinements and improvements. Through this iterative testing process, designers ensure that the final product is not only functional but also resonates with the end-users.
Application of Human-Centric Design: Successful Businesses
Apple: Seamlessly Integrating Technology into Daily Life


Duolingo: Making Language Learning Engaging and Accessible


Duolingo has disrupted the language learning landscape by applying Human-Centric UX Design principles. The app employs gamification elements, short lessons, and personalized learning paths to engage users effectively. The empathy-driven approach is evident in Duolingo’s understanding that language learners have varied preferences and time constraints. By offering bite-sized lessons and a visually appealing interface, Duolingo caters to the diverse needs of its users. Regular updates and improvements based on user feedback further demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement and a user-centered mindset.
Spotify: Tailoring Music Experiences to Individual Tastes

Human-Centric Design in the Developing Era of AI: Challenges and Solutions


Challenges
Ethics and Inclusivity: Maintaining Ethical Standards and Inclusiveness
As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated, the ethical implications of their use within the context of Human-Centered Design are paramount. Designers face the challenge of ensuring that AI applications are developed and deployed in ways that align with ethical standards, respect privacy, and uphold inclusivity. The potential biases embedded in AI algorithms pose a significant concern, requiring designers to be vigilant in addressing and mitigating biases to prevent discrimination. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical considerations is crucial to building trust among users and fostering a positive relationship between technology and humanity.
Balancing Objectives: Merging User Needs with Organizational Aspirations
The challenge of harmonizing user-centric objectives with organizational goals is magnified in the context of AI development. Human-Centered Design traditionally places user needs at the forefront, but the integration of AI may introduce complexities tied to business objectives. Designers must navigate the delicate balance between creating AI systems that cater to user preferences and advancing organizational interests. This involves aligning AI capabilities with user expectations while ensuring that business objectives are met, avoiding scenarios where AI solutions are perceived as intrusive or driven solely by profit motives.
Complex Stakeholder Landscape: Dealing with Complex Problems Involving Several Parties
The development and implementation of AI solutions often involve a myriad of stakeholders, each with distinct interests and perspectives. This complex landscape poses a challenge for Human-Centered Designers, as they need to navigate diverse stakeholder expectations, including users, developers, business leaders, and regulatory bodies. Maintaining open lines of communication, fostering collaboration, and understanding the unique requirements of each stakeholder group are critical aspects of managing the intricate web of relationships in AI development. This challenge underscores the importance of comprehensive research and iterative design processes to address the diverse needs of all stakeholders.
Depth vs. Surface: Addressing Underlying Issues Beyond Surface-level Interaction
Human-Centered Design in the era of AI demands a shift from surface-level interactions to a more profound understanding of underlying issues. Designers must move beyond creating user interfaces and experiences that merely scratch the surface, delving into the intricacies of how AI systems function and impact users. This involves addressing issues such as algorithmic transparency, accountability, and the societal implications of AI. Striking a balance between delivering user-friendly interfaces and addressing the deeper complexities of AI-driven interactions is essential to create solutions that are both user-centric and ethically robust.
SmartDev: Partnering for Human-Centered UX Design Excellence


User Engagement: Consistently Involving End-Users
SmartDev recognizes that sustained user engagement is crucial for successful UX design. The company employs an iterative and collaborative approach, actively involving end-users in every phase of the UX Design Roadmap. Through user interviews, usability testing, and feedback loops, SmartDev ensures that user perspectives guide the design process. This commitment to user involvement fosters a sense of co-creation, leading to solutions that genuinely resonate with end-users.
Empathy at the Core: Understanding the End-User Experience
Through immersive research methods and user-centric design thinking, SmartDev’s teams put themselves in the shoes of the users, ensuring that the design solutions not only meet functional requirements but also address the emotional and experiential aspects of the user journey.
Cross-Sector Collaboration: Teaming Up with Varied Stakeholders
By facilitating open communication and collaboration, SmartDev ensures that the design process benefits from the collective insights of developers, designers, business leaders, and end-users. This collaborative approach results in holistic solutions that consider a broad spectrum of perspectives.
Ethical Framework: Incorporating a Code of Ethics
Ethical considerations are indispensable factors in SmartDev’s design philosophy. The company incorporates a robust code of ethics into its human-computer interaction (HCI) design. This framework guides decision-making, ensuring that AI applications and digital solutions align with principles of fairness, transparency, and user privacy. By adhering to a strong ethical foundation, SmartDev builds trust and confidence in its designs.
Data-Driven Outcomes: Using Evidence for Informed Design Decisions
The company leverages evidence and analytics to inform design decisions and measure outcomes. By relying on quantitative and qualitative data, SmartDev ensures that the UX design is not only intuitive but also aligned with user preferences and behaviors. This iterative, data-driven approach contributes to the continuous improvement of user experiences.
Conclusion
In the dynamic realm of AI, Human-Centric UX Design has evolved from a trend to a fundamental necessity, and the emphasis on understanding and catering to the diverse needs of end-users has become instrumental in the success of IT projects and products. In closing, it’s abundantly clear that prioritizing the user experience isn’t just a strategy; it’s a transformative game-changer reshaping the very landscape of AI and digital innovation. The journey toward a future where technology seamlessly aligns with human intuition and needs starts with SmartDev—a true catalyst for change Contact us now at [email protected] to discover how SmartDev can revolutionize your AI projects with user-centric, ethical, and innovative digital experiences. Let’s revolutionize the future of AI with SmartDev’s expertise in creating user-centric, ethical, and innovative digital experiences.